In the ever-evolving landscape of medical diagnostics, Esophageal Manometry emerges as a powerful tool, providing crucial insights into the functioning of the esophagus. This article aims to demystify Esophageal Manometry, exploring its significance, applications, and the detailed process involved in this diagnostic procedure.
What is Esophageal Manometry?
Esophageal Manometry is a diagnostic test designed to evaluate the muscular function and coordination of the esophagus. This procedure is particularly instrumental in identifying and diagnosing various esophageal disorders, ranging from motility issues to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).

Esophageal Manometry
Why is Esophageal Manometry Important?
- Accurate Diagnosis: Esophageal Manometry plays a pivotal role in accurately diagnosing conditions such as achalasia, a disorder characterized by impaired esophageal motility. It provides healthcare professionals with critical data to differentiate between various esophageal disorders.
- Tailored Treatment Plans: By precisely measuring the pressure exerted by the esophageal muscles, this test allows medical professionals to tailor treatment plans to address the specific needs of each patient. This personalized approach enhances the effectiveness of interventions.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Evaluation: Esophageal Manometry is particularly valuable in evaluating the extent and severity of gastroesophageal reflux. The data obtained aids in determining the most appropriate treatment strategies, whether medical, surgical, or lifestyle modifications.
How is Esophageal Manometry Conducted?
The procedure involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube with pressure sensors through the nose and into the esophagus. This tube measures the muscular contractions and relaxations of the esophageal muscles as they propel food towards the stomach. Patients may be asked to swallow at specific intervals during the test to assess the coordination of these movements.
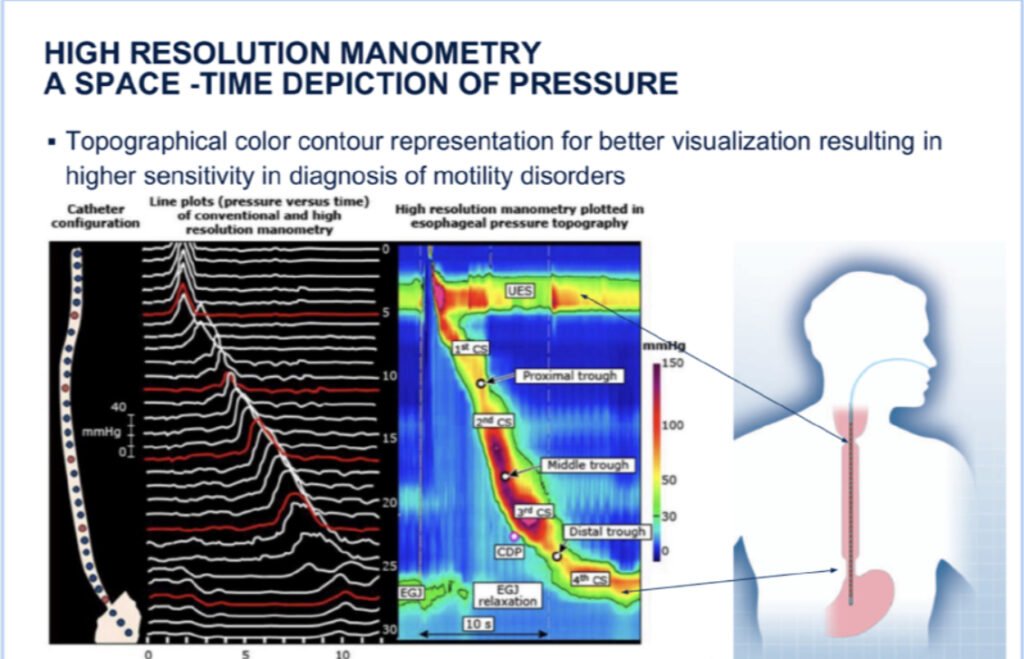
Key Steps in Esophageal Manometry:
- Preparation: Patients are usually advised to fast for a specified period before the procedure to ensure accurate results. It’s essential to inform healthcare providers about any medications being taken, as some may need to be temporarily discontinued.
- Insertion of the Catheter: A catheter, equipped with pressure sensors, is gently inserted through the nose and into the esophagus. This process is minimally invasive and well-tolerated by most patients.
- Data Collection: As the patient swallows, the sensors on the catheter measure the pressure exerted by the esophageal muscles, providing a comprehensive picture of their function and coordination.
Why it’s Necessary:
Your healthcare provider may suggest esophageal manometry if you’re experiencing symptoms that may be indicative of an esophageal disorder.
This diagnostic procedure offers insights into the passage of food from the esophagus to the stomach. It assesses the functionality of the sphincter muscles at both ends of your esophagus, measuring their opening and closing abilities. Additionally, esophageal manometry gauges the pressure, speed, and pattern of the muscular contractions that propel food through the esophagus.
When difficulty swallowing or painful swallowing is your primary concern, your doctor may initially recommend alternative tests such as X-rays or upper endoscopy. These tests, conducted before or in lieu of esophageal manometry, aim to identify or rule out potential issues like narrowing, complete blockage, or inflammation in the esophagus.
Esophageal manometry is instrumental in diagnosing various conditions, including:
- Diffuse Esophageal Spasm: Characterized by uncoordinated muscle contractions, this rare swallowing problem is effectively assessed through esophageal manometry.
- Achalasia: This infrequent condition arises when the lower esophageal sphincter muscle fails to relax properly, leading to difficulties in swallowing and food regurgitation.
- Scleroderma: For individuals with this rare progressive disease, esophageal manometry aids in detecting halted movement in the lower esophagus muscles, often associated with severe gastroesophageal reflux.
In cases where anti-reflux surgery is recommended for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), esophageal manometry becomes crucial. It helps ensure that conditions like achalasia or scleroderma, which GERD surgery cannot address, are ruled out.
For individuals experiencing non-cardiac chest pain unresponsive to GERD treatment, esophageal manometry may be suggested as part of the diagnostic process.
Conclusion:
Esophageal Manometry stands at the forefront of diagnostic tools, providing invaluable information for healthcare professionals. This procedure, while minimally invasive, yields detailed insights that enable accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans. As technology continues to advance, Esophageal Manometry remains an essential component of modern gastroenterological care, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients with esophageal disorders.
🌟 Uncover Wellness in Agra: Experience the Power of Esophageal Manometry! 🌟
If you experiencing discomfort or uncertainty about your digestive health in the enchanting city of Agra? Look no further – Esophageal Manometry is here to bring clarity and personalized solutions to your doorstep!
Conveniently Located: Our center in the only center in Agra , which offers this facility bringing advanced healthcare closer to you. No need to travel far for top-notch diagnostics – we’re right here in the City of Taj!

Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.